What is Kardex, what is it for and how is it used?
The Kardex is a fundamental tool in inventory management and business administration. Its origin dates back to manual accounting systems, where cards were used to record the movement of products in a warehouse. Today, the Kardex has been digitized, becoming an essential part of modern inventory systems. But what exactly is the Kardex, what is it for, and how is it used? In this article, we will explore these questions in detail.
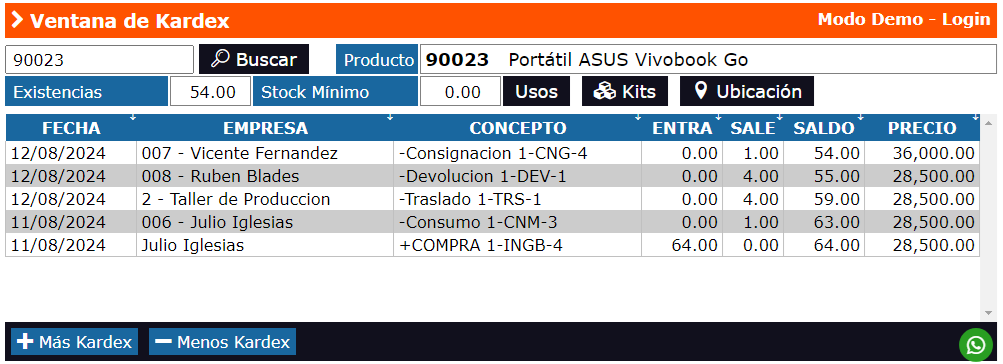
What is the Kardex?
The Kardex is a detailed record that allows you to keep track of inventory movements of a company. This record includes information about:
- Entries: Quantities of products that enter the inventory, either by purchases, returns, or production.
- Exits: Quantities of products that leave the inventory, either by sales, internal consumption, or losses.
- Balances: Remaining quantities of products after each movement.
In simple terms, the Kardex functions as a logbook that details how and when each product moves within an organization.
What is the Kardex used for?
The Kardex is essential for:
- Inventory control: It helps to avoid shortages or excesses of products, ensuring that there are always enough stocks to meet demand.
- Decision making: It provides key data to determine when to restock a product or how to optimize storage.
- Fiscal compliance: In many countries, the Kardex is a legal requirement to justify inventory movements before tax authorities.
- Cost reduction: It allows identifying products with low turnover, avoiding unnecessary investments.
- Transparency: It facilitates internal and external audits by having a clear and organized record.
How is the Kardex used?
The use of the Kardex may vary depending on the type of business and the tools used, but generally follows these steps:
1. Product registration
Before starting to use the Kardex, it is necessary to register all the products that are part of the inventory. Each product must have a unique code, a clear description, and in some cases, a category or location in the warehouse.
2. Movement input
Each time a product enters or leaves the inventory, it is registered in the Kardex. The information that is usually included is:
- Date of the movement.
- Movement description (purchase, sale, return, etc.).
- Quantity of units.
- Unit price and total value.
- Updated balance after the movement.
3. Cost calculation
The Kardex also allows calculating the cost of the products using methods such as:
- FIFO (First In, First Out): The cost of the first units entered into the inventory is assigned.
- LIFO (Last In, First Out): The cost of the last units entered is assigned.
- Weighted average: A weighted average cost is calculated based on all entries.
4. Periodic review
It is important to review the Kardex periodically to ensure that the information is accurate and matches the physical inventory.
Practical example
Suppose you have a clothing store and register the inventory of t-shirts. If you buy 100 t-shirts at $10 each and then sell 20 at $15 each, the Kardex would look something like this:
| Date | Movement | Quantity | Unit Price | Total Value | Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01/01/2024 | Purchase | +100 | $10 | $1,000 | 100 |
| 02/01/2024 | Sale | -20 | $10 | $200 | 80 |
Tools for managing the Kardex
Today, there are multiple digital tools for managing the Kardex efficiently. Some systems, such as our Inventarios1A software, automate this process, allowing you to register movements, calculate costs, and manage reports with just a few clicks. Additionally, you can check your inventory in real-time from any device, which facilitates decision-making.
The Kardex is much more than a simple record; it is a strategic tool for any business that manages inventories. Its correct use can make the difference between efficient management and operational chaos. If you still do not use a Kardex system in your company, what are you waiting for? It's time to optimize your processes and take your inventory management to the next level.






